Pistachios grow in grape-like clusters on the tree and each cluster may have anywhere from thirty to fifty nuts. The pistachio is a broad, bushy, deciduous tree which grows slowly to a height and spread of 25 to 30 feet, with one or several trunks. They require both male and female trees for the fruit to grow and winds to spread the pollen. Under favorable conditions pistachio trees live and produce for centuries.
Pistachio is cultivated for nut production and the nuts are mainly used for eating out of hand as fresh, dried, and roasted with or without salt and flavorings.
A fully mature and naturally ripened pistachio nut (embryo or seed). With the shell(endocarp). naturally split and the hull (internal mesocarp) puffed and turning red
What is pistachio
Pistachio is a nutritious nut and a member of the cashew family that originated from central Asia and the middle east, and some countries are famous for exporting it.
The genus Pistacia L. consists of 11 or more tree and shrub species belonging to the Anacardiaceae, family. Pistacia vera L. is the only commercially-important species within this genus with nuts large enough to be consumed. The center of diversity of P. vera is northern Iran, southern Turkmenistan and parts of Afghanistan. Botanically, pistachio fruits are semidry drupes composed of a fleshy excerpt and monocarp (pericarp or hull), and a hard endocarp (shell) containing the edible kernel. Pistachio is a wind pollinated dioecious tree with apetalous pistillate and staminate inflorescences on separate female and male trees. Currently pistachio cultivation is expanding in Iran, the USA, Turkey, Greece, Italy, Spain, China, Tunisia and many other countries

The Shape and Taste
Pistachios are nutritious nuts that are sorted based on the shape of their shell into two categories: Open-mouth and Closed-mouth. The open-mouth pistachios are higher in price, value, and demand than the closed-mouth pistachios.
There are many types of pistachios, depending on the type and place of growth; they have different sizes, colors, and flavors. Depending on the shape of the pistachio, it can be divided into three general categories: round, long, and jumbo Long pistachios have a narrower split than the other two, and the round and jumbo type have a much clearer split than the semi-closed one. Fig 1 shows a summary of pistachios’ different types
different types of pistachios:
- S:Kerman,platinum,pioneer gold,jolry,red allepo,
- Iran: Akbari, Ahmad Aghaii, Fandoughi, and Kalehghouchi
- Syria: Red Aleppo
- Turkey: Uzun and Kirmizi Sicily: Napoletana, Siirt
- Australia: Sirora
Pistachio varieties from some other countries are meant to have better taste than the ones grown in California (especially Kerman pistachio from Iran).
Pistachio taste can be influenced by:
- Genetic diversity in sugar, oils and other constituents of the nut
- By climate and cultural practices that affect nut size, for instance.
Maintenance method
The best way to store nuts is to store them in the freezer to prevent aflatoxin from growing on the surface of the seeds and kernels.
5 Culinary Uses of Pistachios
The kernels are often eaten whole, either fresh or roasted and salted, and are also used in:
- As a snack.
- Over salads.
- Ground into sauces. …
- Added to bread dough. …
- confections such as baklava,
- Yogurt
- Nut butter
History
Pistachios have been part of the human diet since prehistoric times and have been consumed by past civilizations because of their nutritional and potential disease-management properties.
Native to the Middle East, the pistachio tree is one of the oldest flowering nut trees. Archeological records of early human pistachio consumption in Turkey date back to as early as 7,000 B.C. Flourishing in hot climates, pistachio trees spread from the Middle East to the Mediterranean,
Pistachio, native to West Asia, Asia Minor, a place that still grows occasionally, can be found in the hot and dry conditions of Lebanon, Palestine, Syria, Iran, Iraq, India and southern Europe, and the desert farms of Asia and Africa.
Pistachios were imported to Europe early in the Gregorian calendar. The first introduction of pistachios to the United States by the USDA (Plant Identification Service) in 1890 budget. In 1904, he arrived in California as Prime Minister at the Gia Mall in Chicago, northern Sacramento, California.
Benefits
Health is an important pillar of human life and the pistachio is among the nuts which have an impact on human health
- CARDIOVASCULAR HEALTH
- Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects
- control blood pressure
- help lower blood sugar
- GLYCEMIC CONTROL AND TYPE 2 DIABETES
- WEIGHT CONTROL
nuts such as pistachio have many beneficial effects on health, and can be used for controlling different diseases. It seems that the pistachio may have anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic, anti-hyperlipidemia, and anti-proliferation effects and may be recommended for the prevention, improvement, or treatment of diseases such as diabetes, CVD, inflammatory bowel disease (IBS), cancer, and MS.
Loaded with nutrients
with a 1-ounce (28-gram) serving of about 49 pistachios containing the following:
- Calories: 159
- Carbs: 8 grams
- Fiber: 3 grams
- Protein: 6 grams
- Fat: 13 grams (90% are unsaturated fats)
- Potassium: 6% of the Reference Daily Intake (RDI)
- Phosphorus: 11% of the RDI
- Vitamin B6: 28% of the RDI
- Thiamine: 21% of the RDI
- Copper: 41% of the RDI
- Manganese: 15% of the RDI
pistachios are one of the most vitamin B6-rich foods .
They also pack quite a punch of potassium. In fact, a 2-ounce serving has more potassium than a large banana and as much fiber as a cup of cooked broccoli.
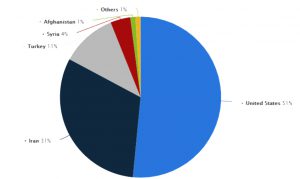
Exporting pistachios
In 2014, Iran was recognized as the largest exporter of this product in the world with more than 191 thousand tons of exports. The United States also became the world’s second largest pistachio exporter in 2014, exporting about 138,000 tons. Turkey is the third largest exporter of pistachios in the world. Turkey ranked third in the world in 2014, risking about 3,000 tons and exporting
In 2018, the global production of pistachios was about 1.4 million tons.
Iran and the United States as leading producers, together 72% of the total (table). another producers were Turkey, China, and Syria.